Manufacturing has come a long way since the industrial revolution.
Mechanisation and steam power paved the way for mass production, which has since evolved into automation, robotics and digitised manufacturing systems. Recent technological developments are continuing to transform the sector in a few key ways.
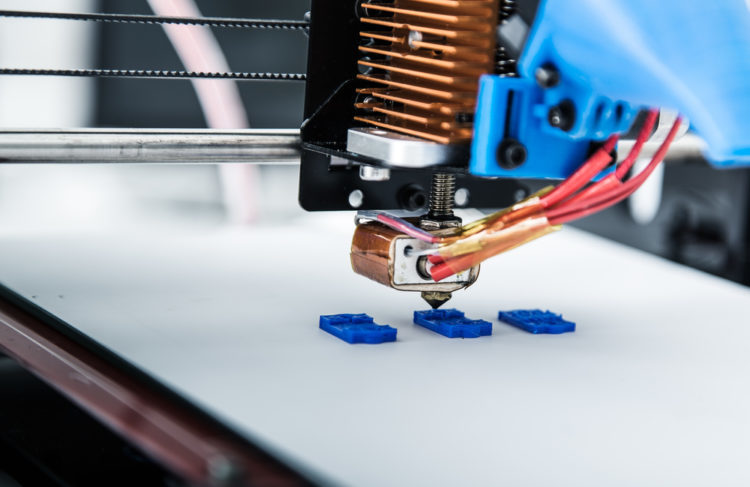
Additive manufacturing
New techniques are diversifying and increasing production capabilities. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is an innovative technology that facilitates the creation of items and components with a computer-controlled layering system.
These systems can cut the cost of manufacturing low volumes and prototypes, while also reducing waste and production times. It’s currently limited to certain materials and volumes, but the potential of this technology to boost manufacturing capabilities is significant.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that represents networks of devices connecting the physical world to the digital. State-of-the-art single-board computers such as the Rock Pi and more advanced hardware systems are often used to connect devices and software via IoT. In industrial settings, it’s being deployed to monitor and transform manufacturing processes and supply chains.
Digital devices such as sensors, cameras, alarms and smart appliances are connected to networks that allow real-time data collection and analysis to improve the efficiency of manufacturing systems. For example, sensors installed on machinery can help to foresee breakdowns to reduce production line downtime, boosting cost per unit and efficiency metrics.
Augmented reality
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being integrated into many industries, but their applications are less well-known in manufacturing. However, these technologies are changing the face of design and technical engineering.
Rapid prototyping can be carried out with virtual models in AR to speed up the process from initial concepts to physical manifestations. This also helps product and system testing to allow technical aspects to be evaluated without the need for handling physical components.
Big data
The power of data analysis continues to be harnessed in the manufacturing sector. Real-time and detailed analysis of data from machinery, networks and human operators makes for easier optimisation. Greater statistical visibility also improves decision-making and makes manufacturing more responsive to market demands.
Big data capabilities also help to keep track of metrics such as power and resource consumption, so businesses can look to streamline operations and reduce unnecessary carbon emissions. This is a significant advancement in helping industry to contribute more to reaching net zero goals.
Industries that are embracing key technologies such as additive manufacturing, IoT, big data, and even augmented reality to innovate their operations are seeing substantial strides in business development and efficiency. Although technology is constantly evolving and enhancing our capabilities within the world of manufacturing, recent technological developments have seen substantial augmentations in product quality, time-to-market, and the economy of production processes.